Overview Of Components
- Program
- EDB
- Registers
- MCC
- RAM
- DIMM
- RAM Speed
- CPU And CPU Sockets
- CPU Socket
- LGA
- PGA
- Clock/Clock-wire
- Can I increase the clock cycles in the CPU?
- Motherboards
- Chipsets in Motherboard
- PCIE
- Form Factor
- Storage
- HDD
- SSD
- SATA
- Peripherals
- Different Between Megabits and Megabytes per second
- USB Type C
- Relationship Between BIOS and CMOS
- BIOS
- CMOS
Program
The set of instructions that performs the specific task.
External Data Bus (EDB):- EDB is the row of wires that interconnects the parts of our computer, it is just like a vein in our body. when we send a voltage to a wire this means the state of the wire is on or represented by a 1. If there is no voltage then we say that the state is off, represented by 0.
The EDB comes in different sizes, 8 bits, 16 bits, 32 bits, and 64 bits. EDB with 8 bits sending 1 byte at a time. Our CPU receives a byte and it needs to get to work.
Registers:- Register is a component inside the CPU. It stores the data on which the CPU works. Suppose we want to add two digits A and B, and The sum of these digits is C. Now the digit A would be stored in Register 'a' and the digit B would be stored in Register 'b'. The resultant number C would be stored in Register 'c'. Our program is stored in RAM so that the CPU reads the data and processes it then gives the expected result that the user wants.
Through EDB we can send one line of data at a time.
Memory Controller Chip or MCC:- The MCC acts as a bridge between the CPU and the RAM. Whenever the CPU requires some data, it talks to MCC. The MCC finds that data in RAM and grabs the data and sent it through the EDB(External Data Bus).
Address Bus:- It is a type of bus that connects the CPU and the MCC. It sends the location or address of the data. Then the MCC takes the address and looks for the data and then data is sent over EDB.
RAM
RAM is not the fastest way to get the data for processing. The CPU also uses another memory called Cache.
A cache is smaller than RAM, but it is faster than RAM. It is used to store recent data and provide the data quickly to the CPU. There are three different levels of cache in a CPU, L1, L2, and L3.
L1 is the smaller and fastest cache.
Random Access Memory is volatile in nature, which means that once the power is off, the stored data in RAM is cleared. Suppose we have a phone with 16 Gigs of RAM, which means it can run up to 16 gigs of programs. We can run lots of programs at the same time. when we type something in a document, at that time we are using RAM memory. This is primary memory or temporary storage.
There are lots of types of RAM but here we will discuss only advanced types
1. DRAM:- Dynamic Random Access Memory
2. SDRAM:- Synchronous DRAM
SDRAM is synchronized to the system's clock speed. It allows quick processing of the data.
Today's computers have another type of RAM, called DDR SDRAM (Double Dual Rate SDRAM).
It is also called a DDR.

There are lots of types of DDR
DDR1
DDR2
DDR3
DDR4
DDR is faster and has a large capacity than SDRAM. It also takes less power. The latest version of DDR is DDR4. It is the fastest type of memory that is used in a modern computer. Fastest RAM means it provides the data to the user quickly and run more program at the same time. Every RAM sticks need a compatible motherboard.
DIMM:- Dual Inline Memory Module, This is a type of slot in which RAM is fitted. It comes with different sizes of pins on the motherboard.
RAM Speed
Suppose we have RAM sticks on which PC-3200 is written.
that means It has a 400 MHz clock speed
so that 400 Mhz * 8 bytes = 3200 MB per second
that is mentioned on RAM.
CPU and CPU Sockets
The human body performs any specific task with the help of its brain. It gives some instruction to hand to do some task. Our mind takes that instruction, processes it, and gives expected results.
In the same way, if we assume that a computer is a body then the CPU is the brain of that body. It does the same thing as our mind but it all happens with the help of users. CPU has a set of instructions and according to user input, it performs specific work on that instruction and shows the result to users that they want.
A lot of functions like adding, subtracting, copying, and pasting the data are included in the CPU. Any instructions that are simple or complex, the CPU breaks down into small instructions and makes them simple then processing them.
Instruction sets in the CPU are hardcoded. Different CPU manufacturers have different instruction sets But they perform the same functions on particular data. The selection of the CPU should be compatible with the motherboard.
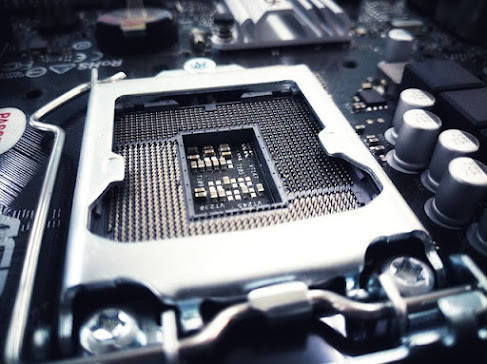
CPU Sockets
The sockets in which the CPU is fit are called CPU sockets. Different motherboards have different types of sockets but make sure the CPU needs the compatible sockets in motherboards.
There are currently two types of CPU sockets
1. Land Grid Array (LGA)
2. Pin Grid Array (PGA)
LGA
It is a type of surface-mount packaging. It is connected electrically to the printed circuit board (PCB). To connect the socket, it is soldered directly to the board.
PGA
It is a type of integrated circuit packaging. It is a rectangle or square in shape. The pins having the size of 2.54 mm are arranged in a regular array on the package. CPU is kept on these pins carefully. PGA socket is not placed by soldering. It is mounted on PCB through the hole method.
Clock/ Clockwire
Our computer CPU has an internal clock that syncs the data operation in the CPU. This clock is connected through a special wire called clock wire. When we send or receive data, it sends a voltage to the clock wire to let the CPU know it can start processing the data. Clock wire acts as the ticking of a clock. For every tick, The CPU does one cycle of operations, when you send a voltage to the clock wire, it is called a clock cycle. If we have lots of data for processing, we need to run lots of clock cycles.
some times you see the CPU is labeled 3.4 GHz. This number tells the clock speed of the CPU. It handles 3.4 billion cycles per second.
Can I increase the clock cycles in the CPU?
There is a way we can increase the number of clock cycles. The exceeded speed of the clock's cycles is referred to as overclocking. Overclocking increases the rate of CPU clock cycles. After overclocking the CPU performs more tasks.
When we do overclock this means we are operating the system outside the limits of the CPU. It could reduce the lifespan of the CPU. Overclocking affects its warranty also. Some companies like AMD and INTEL typically don't cover overclocking, Even Motherboard manufacturers may or may not cover overclocking of the Cpu.
Motherboards
The board holds all physical components together. It helps to expand the functionality of the computer by adding the expansion card and it allows to communicate the different parts of the computer like hardware or software to each other. A key component that allows managing the data between CPU, RAM, and peripherals is called Chipsets.
A peripheral is an external device that connects to our computers like a mouse, a keyboard, and a monitor.
Chipsets in Motherboard
The chipset on motherboards is made up of two chips
1. Northbridge:- RAM, video cards, and CPU are connected to Northbridge.
2. Southbridge:- Input/Output controllers like hard drives and USB devices are connected to Southbridge.
In modern CPU, Northbridge has been directly integrated into the CPU so there are no separate Northbridge chipsets.
The motherboard has an expansion slot. that is used to extend the functionality of the computer.
PCIEForm Factor
In place of ATX, another technology is also used which is ITX or Information Technology Extended form factor. There are the following different types of ITX form factors.
1. Mini ITX
2. Nano ITX
3. Pico ITX
When building the computer it is your choice to select the form factor, keep it small or big according to workload.
Storage
The bit is the smallest data storage A bit can store one or zero digits. A byte is the other largest data storage in computer systems. It is a combination of 8 bits.
A single byte can hold a letter, number, or symbol.
1 Byte = 8 bits
We can store all our data on a hard drive. It allows us to store lots of data like programs, music, pictures, etc. Hard drives store our data somewhere else so that the data may be bucked up if something goes wrong and the hard drive crashes.
There are two types of hard drives to store the data
1. Hard Disk Drive, HDD
2. Solid State Drive, SSD
HDD
Hard Disk Drives use a spinning platter and for reading and writing the information it uses a mechanical arm.
The rotational speed of the platter allows us to read and write data faster. The speed is measured in RPM or Revolution Per Minute. If RPM is high, the data storing and extracting is fast. So always keep in mind while buying a hard drive, see something like 5400 RPM if you buy a 500 gigabytes HDD.Hard Disk drives are is not more expensive. It is a Secondary Storage device.
SSD
A Solid State Drive has no moving parts. There is no platter and no mechanical arm. It has a chip. The data is stored on microchips. It is faster than HDD means extracting and storing the information is fast. SSD has a small form factor compared to HDD.
It has less risk of losing the data. That's why it is more expensive. It also comes under Secondary Storage.
SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment)
SATA is a type of cable that is used to connect the storage device (SSD) and motherboard. It is used to transfer the data and also it helps to provide the power for storage. It has seven pins for data connection and fifteen pins for power connection. The speed of SATA is 6.0 Gbits per second. When we plug in a SATA drive, there is no need to turn off the computer. Therefore it is hot-swappable.Peripherals
Anything that we connect to our system externally helps to extend the functionality of the computer.
We use it on daily basis like USB or Universal Serial Bus. It is the most popular connector. We use it in both cases data transfer and mobile battery charging. There are different types of USB available in the market. But three are the most common these days.
1. USB 2.0:- Transfer speed of 480 megabits per second.
2. USB 3.0:- Transfer speed of 6 gigabits per second.
3. USB 3.1:- Transfer speed of 10 gigabits per second.
If we use to connect a USB 2.0 device to a USB 3.0 port, we won't get a transfer speed of 3.0, But If we connect a USB 3.0 device to a USB 2.0 port, we will get a transfer speed of 2.0.
Different Between Megabits and Megabytes per second
Relationship Between BIOS and CMOS
BIOS
|
Input |
Output |
|
0 |
1 |
|
1 |
0 |















Comments
Post a Comment